设方针A满足矩阵方程(A的平方)-A-2E=0,证明A及A+2E都可逆.
 bmcli2022-10-04 11:39:541条回答
bmcli2022-10-04 11:39:541条回答
设方针A满足矩阵方程(A的平方)-A-2E=0,证明A及A+2E都可逆.
为什么是这样想的呢?其思路是甚么?最重要的是甚么?
为什么是这样想的呢?其思路是甚么?最重要的是甚么?

已提交,审核后显示!提交回复
共1条回复
 ynynyn999 共回答了21个问题
ynynyn999 共回答了21个问题 |采纳率95.2%- A^2-A-2E=0 --> A(A-E)=2E 所以A的逆为(A-E)/2
A^2-A-2E=0 --> (A+2E)(A-3E)=-4E (A+2E)的逆就是(A-3E)/-4 - 1年前
相关推荐
- 确定开展土地革命和武装反抗国民党反动统治的总方针的会议是 [ ] A.遵
确定开展土地革命和武装反抗国民党反动统治的总方针的会议是 [ ]A.遵义会议
B.中共二大
C.八七会议
D.瓦窑堡会议 桅子1年前1
桅子1年前1 -
 inrs 共回答了13个问题
inrs 共回答了13个问题 |采纳率92.3%C1年前查看全部
- common law system 的具体实行方针以及程序(英语回答)
common law system 的具体实行方针以及程序(英语回答)
普通法在英美***的使用情况以及这些法律在审判过程中的具体的步骤! ryfeey1年前1
ryfeey1年前1 -
 VIP雪蓝 共回答了18个问题
VIP雪蓝 共回答了18个问题 |采纳率83.3%The common law forms a major part of the law of those countries of the world with a history as British territories or colonies. It is notable for its inclusion of extensive non-statutory law reflecting precedent derived from centuries of judgments by working jurists.
There are three important connotations to the term.
One is used to distinguish the authority that promulgated a particular proposition of law: for example, the United States typically has "statutes" enacted by a legislature, "regulations" promulgated by executive branch agencies pursuant to a delegation of rule-making authority from a legislature, and "common law" decisions issued by courts (or quasi-judicial tribunals within agencies) that discuss and decide the fine distinctions in statutes and regulations. See statutory law and non-statutory law.
The second distinguishes "common law" jurisdictions (most of which descend from the English legal system) that place great weight on such common law decisons, from "civil law" or "code" jurisdictions (many of which descend from the Napoleonic code in which the weight accorded judicial precedent is much less).
The third distinguishes "common law" (or just "law") from "equity". Until the beginning of the 20th Century, most common law jurisdictions had two parallel court systems, courts of "law" that could only award money damages and recognised only the legal owner of property, and courts of "equity" that recognised trusts of property and could issue injunctions, orders to do or stop doing something. Although the separate courts were merged long ago in most jurisdictions, or at least all courts were permitted to apply both law and equity, the distinction between law and equity remains important in (a) categorising and prioritising rights to property, (b) determining whether the Seventh Amendment's guarantee of a jury trial applies (a determination of a fact necessary to resolution of a "law" claim) or whether the issue can only be decided by a judge (issues of equity), and (c) in the principles that apply to the grant of equitable remedies by the courts.
Many important areas of law are governed primarily by common law. For example, in England and Wales and in most states of the United States, the basic law of contracts and torts does not exist in statute, but only in common law. In almost all areas of the law, statutes may give only terse statements of general principle, but the fine boundaries and definitions exist only in the common law. To find out what the law is, you have to locate precedential decisions on the topic, and reason from those decisions by analogy.
Contents [hide]
1 History of the common law
2 Common law legal systems
3 Basic principles of common law
4 Works on the common law
5 See also
6 External links
[edit]
History of the common law
Common law originally developed under the inquisitorial system in England from judicial decisions that were based in tradition, custom, and precedent. Such forms of legal institutions and culture bear resemblance to those which existed historically in continental Europe and other societies where precedent and custom have at times played a substantial role in the legal process, including Germanic law recorded in Roman historical chronicles. The form of reasoning used in common law is known as casuistry or case-based reasoning. The common law, as applied in civil cases (as distinct from criminal cases), was devised as a means of compensating someone for wrongful acts known as torts, including both intentional torts and torts caused by negligence, and as developing the body of law recognizing and regulating contracts. The type of procedure practised in common law courts is known as the adversarial system; this is also a development of the common law.
Before the institutional stability imposed on England by William the Conqueror in 1066, English residents, like those of many other societies, particularly the Germanic cultures of continental Europe, were governed by unwritten local customs that varied from community to community and were enforced in often arbitrary fashion. For example, courts generally consisted of informal public assemblies that weighed conflicting claims in a case and, if unable to reach a decision, might require an accused to test guilt or innocence by carrying a red-hot iron or snatching a stone from a cauldron of boiling water or some other "test" of veracity (trial by ordeal). If the defendant's wound healed within a prescribed period, he was set free as innocent; if not, execution usually followed.
In 1154, Henry II became the first Plantagenet king. Among many achievements, Henry institutionalized common law by creating a unified system of law "common" to the country through incorporating and elevating local custom to the national, ending local control and peculiarities, eliminating arbitrary remedies, and reinstating a jury system of citizens sworn on oath to investigate reliable criminal accusations and civil claims. The jury reached its verdict through evaluating common local knowledge, not necessarily through the presentation of evidence, a distinguishing factor from today's civil and criminal court systems.
Henry II's creation of a powerful and unified court system, which curbed somewhat the power of canonical (church) courts, brought him (and England) into conflict with the church, most famously, with Thomas Becket, the Archbishop of Canterbury. Things were resolved eventually, at least for a time, in Henry's favour when a group of his henchmen murdered Becket. For its part, the Church soon canonized Becket as a saint.
Thus, in English legal history, judicially-developed "common law" became the uniform authority throughout the realm several centuries before Parliament acquired the power to make laws.
As early as the 15th century, it became the practice that litigants who felt they had been cheated by the common-law system would petition the King in person. For example, they might argue that an award of damages (at common law) was not sufficient redress for a trespasser occupying their land, and instead request that the trespasser be evicted. From this developed the system of equity, administered by the Lord Chancellor, in the courts of chancery. By their nature, equity and law were frequently in conflict and litigation would frequently continue for years as one court countermanded the other, even though it was established by the 17th century that equity should prevail. A famous example is the fictional case of Jarndyce and Jarndyce in Bleak House, by Charles Dickens.
In England, courts of law and equity were combined by the Judicature Acts of 1873 and 1875, with equity being supreme in case of conflict. In the United States, parallel systems of law (providing money damages) and equity (fashioning a remedy to fit the situation) survived well into the 20th century in most jurisdictions. The United States federal courts separated law and equity until they were combined by the Federal Rules of Civil Procedure in 1937 - the same judges could hear either kind of case, but a given case could only pursue causes in law or in equity, which of course led to all kinds of problems when a given case required both money damages and injunctive relief. Delaware still has separate courts of law and equity, and in many states there are separate divisions for law and equity within one court.
[edit]
Common law legal systems
The common law constitutes the basis of the legal systems of: England and Wales, the Republic of Ireland, federal law in the United States and the states' laws (except Louisiana), federal law in Canada and the provinces' laws (except Quebec civil law), Australia, New Zealand, South Africa, India, Sri Lanka, Malaysia, Brunei, Pakistan, Singapore, Hong Kong, and many other generally English-speaking countries or Commonwealth countries. Essentially, every country which has been colonised at some time by Britain uses common law except those that had been colonized by other nations, such as Quebec (which follows French law to some extent) and South Africa (which follows Roman Dutch law), where the prior civil law system was retained to respect the civil rights of the local colonists. India's system of common law is also a mixture of English law and the local Hindu law.
The main alternative to the common law system is the civil law system, which is used in Continental Europe, and most of the rest of the world. The former Soviet Bloc and other Socialist countries used a Socialist law system.
The opposition between civil law and common law legal systems has become increasingly blurred, with the growing importance of jurisprudence (almost like case law but in name) in civil law countries, and the growing importance of statute law and codes in common law countries (for example, in matters of criminal law, commercial law (the Uniform Commercal Code in the early 1960's) and procedure (the Federal Rules of Evidence in the 1970's)).
Scotland is often said to use the civil law system but in fact it has a unique system that combines elements of an uncodified civil law dating back to the Corpus Juris Civilis with an element of common law long predating the Treaty of Union with England in 1707. Scots common law differs in that the use of precedents is subject to the courts seeking to discover the principle which justifies a law rather than to search for an example as a precedent and that the principles of natural justice and fairness have always formed a source of Scots Law. Comparable pluralistic legal systems operate in Quebec, Louisiana and South Africa. These systems are referred to as mixed legal systems.
The U.S. state of California has a system based on common law, but it has codified the law in the manner of the civil law jurisdictions. The reason for the enactment of the codes in California in the nineteenth century was to replace a pre-existing system based on Spanish civil law with a system based on common law, similar to that in most other states. California and a number of other Western states, however, have retained the concept of community property derived from civil law. The California courts have treated portions of the codes as an extension of the common-law tradition, subject to judicial development in the same manner as judge-made common law. (Most notably, in the case Li v. Yellow Cab Co., 13 Cal.3d 804 (1975), the California Supreme Court adopted the principle of comparative negligence in the face of a California Civil Code provision codifying the traditional common-law doctrine of contributory negligence.)
The state of New York, which also has a civil law history from its Dutch colonial days, also began a codification of its laws in the 19th century. The only part of this codification process that was considered complete is known as the Field Code applying to civil procedure. The original colony of New Netherlands was settled by the Dutch and the law was also Dutch. When the British captured pre-existing colonies they continued to allow the local settlers to keep their civil law. However, the Dutch settlers revolted against the English and the colony was recaptured by the Dutch. When the English finally regained control of New Netherlands -- as a punishment unique in the history of the British Empire -- they forced the English common law upon all the colonists, including the Dutch. This was problematic as the patroon system of land holding, based on the feudal system and civil law, continued to operate in the colony until it was abolished in the mid-nineteenth century. The influence of Roman Dutch law continued in the colony well into the late nineteenth century. The codification of a law of general obligations shows how remnants of the civil law tradition in New York continued on from the Dutch days.
[edit]
Basic principles of common law
Statutes which reflect English common law are understood always to be interpreted in light of the common law tradition, and so may leave a number of things unsaid because they are already understood from the point of view of pre-existing case law and custom. This can readily be seen in the area of criminal law, which while remaining largely governed by the common law in England, has been entirely codified in many US states. Codification is the process where a statute is passed with the intention of restating the common law position in a single document rather than creating new offences, so the common law remains relevant to their interpretation. This is why even today American law schools teach the common law of crime as practised in England in 1750, since the colonies (and subsequently the states) deviated from the common law as practised in England only after that date.
By contrast to the statutory codifications of common law, some laws are purely statutory, and may create a new cause of action beyond the common law. An example is the tort of wrongful death, which allows certain persons, usually a spouse, child or estate, to sue for damages on behalf of the deceased. There is no such tort in English common law; thus, any jurisdiction that lacks a wrongful death statute will not allow a lawsuit for the wrongful death of a loved one. Where a wrongful death statute exists, the damages or compensation available are limited to those outlined in the statute (typically, an upper limit on the amount of damages). Courts generally interpret statutes that create new causes of action narrowly -- that is, limited to their precise terms -- because the courts generally recognize the legislature as being supreme in deciding the reach of judge-made law unless such statute should violate some "second order" constitutional law provision (compare judicial activism).
Where a tort is rooted in common law, then all damages traditionally recognized historically for that tort may be sued for, whether or not there is mention of those damages in the current statutory law. For instance, a person who sustains bodily injury through the negligence of another may sue for medical costs, pain, suffering, loss of earnings or earning capacity, mental and/or emotional distress, loss of quality of life, disfigurement, and more. These damages need not be set forth in statute as they already exist in the tradition of common law. However, without a wrongful death statute, most of them are extinguished upon death.
[edit]
Works on the common law
The definitive historical treatise on the common law is Commentaries on the Laws of England, written by Sir William Blackstone and first published in 1765 - 1769. Since 1979 a facsimile edition of that first edition has been available in four paper-bound volumes. Today it has been superseded in the English part of the United Kingdom by Halsbury's Laws of England that covers both common and statutory English law.
While he was still on the Massachusetts Supreme Judicial Court, and before being named to the U.S. Supreme Court, Justice Oliver Wendell Holmes Jr. published a short volume called The Common Law which remains a classic in the field. In the United States, the Corpus Juris Secundum is a compendium of the common law and its variations throughout the various state jurisdictions. The American Law Institute publishes Restatements of the common law which are often cited by American courts and lawyers when they need to invoke uncodified common law doctrines.
Scots common law covers matters including murder and theft, and has sources in custom, in legal writings and in previous court decisions. The legal writings used are called Institutional Texts and come mostly from the 17th, 18th and 19th centuries. Examples include Craig, Jus Feudale (1655) and Stair, The Institutions of the Law of Scotland (1681).
[edit]
See also
Arraignment
Civil law (legal system)
Common-law marriage
English law
Grand jury
Jury trial
List of legal topics
Scots law
[edit]1年前查看全部
- 调整国民经济的八字方针是什么?
 天天伟伟1年前1
天天伟伟1年前1 -
 madelaine 共回答了8个问题
madelaine 共回答了8个问题 |采纳率100%【八字方针】是中国共产党在开始全面建设社会主义时期提出的恢复与发展国民经济的方针.即“调整、巩固、充实、提高”的方针.1年前查看全部
- 英语翻译中文:确定对外合作项目,要根据自己的条件和特点,符合本社的出版方针和出书范围.我的英语翻译:The identi
英语翻译
中文:确定对外合作项目,要根据自己的条件和特点,符合本社的出版方针和出书范围.
我的英语翻译:
The identification of external cooperation should in accordance with its own conditions and features,meeting the agency's publication policy and scope. gfjttyy1年前1
gfjttyy1年前1 -
 frm0101 共回答了20个问题
frm0101 共回答了20个问题 |采纳率90%Identify external cooperation projects,according to its own conditions and characteristics,with the publication of this agency's policy and published a book of reference1年前查看全部
- 中国象棋棋盘上有“楚河汉界”(如右图),这是怎么来的呢?相传楚汉相争时,刘邦采取斗智不斗力的战略方针,暗中派韩信东度黄河
中国象棋棋盘上有“楚河汉界”(如右图),这是怎么来的呢?相传楚汉相争时,刘邦采取斗智不斗力的战略方针,暗中派韩信东度黄河的同时,长期把项羽兵力牵制在荥阳,迫使项羽“乃与汉约,中分天下,割鸿沟西为汉,东为楚”鸿沟于是成了楚汉的边界。历史把刘邦和项羽争夺帝位的战争称之为()
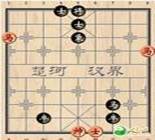
A.巨鹿之战 B.楚汉战争 C.长平之战 D.马陵之战  hmily_03101年前1
hmily_03101年前1 -
 小小游子 共回答了18个问题
小小游子 共回答了18个问题 |采纳率100%B
本题考查的是楚汉战争。历史把刘邦和项羽争夺帝位的战争称之为楚汉战争,故选B。1年前查看全部
- 英语翻译口号,方针里面的内容需要大写吗?首字母大写还是每个词?比如:1.motto "innovative,aggres
英语翻译
口号,方针里面的内容需要大写吗?首字母大写还是每个词?
比如:
1.motto "innovative,aggresive..."
2.motto "(里面是句子,短语)"呢? YHT1221年前3
YHT1221年前3 -
 让你ii唱uu 共回答了15个问题
让你ii唱uu 共回答了15个问题 |采纳率93.3%每个词,除了in, and, of等词
实际上,这样的词语有时候也大写
另外有的标语每个字母都大写1年前查看全部
- 根据“因地制宜”的方针,下列地区应种植的农作物,搭配正确的是
根据“因地制宜”的方针,下列地区应种植的农作物,搭配正确的是
A山东半岛:甘薯,花生 B四川盆地:水稻,甜菜 C松嫩平原:小麦,大豆 D江汉平原:棉花,花生
 樱草1271年前1
樱草1271年前1 -
 A_nan 共回答了19个问题
A_nan 共回答了19个问题 |采纳率78.9%C.松嫩平原——春小麦,甜菜,大豆1年前查看全部
- 防止外来物种入侵应采取的方针是 A.重在宣传教育 B.加强科学研究 C.预防为主,防治结合 D.只种植本地物种
 luluzzw1年前3
luluzzw1年前3 -
 sheniqishui 共回答了16个问题
sheniqishui 共回答了16个问题 |采纳率93.8%是C...某某某某某某1年前查看全部
- 有一实心方针,每边棋子20枚,现增加棋子30枚,摆成五层空心方针,求最外层和最里层各有多少棋子?
有一实心方针,每边棋子20枚,现增加棋子30枚,摆成五层空心方针,求最外层和最里层各有多少棋子?
RT ljh5211年前1
ljh5211年前1 -
 jyhjhgjk 共回答了31个问题
jyhjhgjk 共回答了31个问题 |采纳率83.9%设最外层有 x 枚棋子,则从外到内五层棋子数分别为 x、x-4、x-8、x-12、x-16 ,
实心方针,每边棋子 20 枚,则共有 20*20 枚棋子;
可列方程:x+(x-4)+(x-8)+(x-12)+(x-16) = 20*20+30 ,
解得:x = 94 ,可得:x-16 = 78 ,
即:最外层有 94 枚棋子,最里层有 78 枚棋子.1年前查看全部
- 钟三长的方针长9厘米,这个钟表的分针尖端在1小时里走了多少厘米,分针1小时扫过的面积是多少平方厘米
 稻草uu1年前1
稻草uu1年前1 -
 披云促宴筵 共回答了18个问题
披云促宴筵 共回答了18个问题 |采纳率94.4%分针1小时转一圈
3.14×2×9=56.52(厘米)
3.14×9×9=254.34(平方厘米)
答:分针尖端在1小时里走了56.52厘米,分针1小时扫过的面积是254.34平方厘米1年前查看全部
- 将-4,-3,-2,-1,0,1,2,3,4这9个数分别填入如图中方针的9个空格中,十得横,竖,斜对角的所有3个数相加的
将-4,-3,-2,-1,0,1,2,3,4这9个数分别填入如图中方针的9个空格中,十得横,竖,斜对角的所有3个数相加的和都相等.
表格做不出来,但是答题者可自己做.表格是竖着3个横着3个共三行.
今晚就用拜托我定给积分. 认真看贴1年前3
认真看贴1年前3 -
 芯尔 共回答了17个问题
芯尔 共回答了17个问题 |采纳率100%3 -4 1
-2 0 2
-1 4 -31年前查看全部
- 大跃进后为了纠正·左·倾错误党中央提出什么方针
 lin854301年前1
lin854301年前1 -
 shaojian1987 共回答了18个问题
shaojian1987 共回答了18个问题 |采纳率83.3%大跃进后1960年国家针对国民经济制定了“调整、巩固、充实、提高”八字方针来纠正错误
“八字方针”的基本内容是:调整国民经济各部门的比例关系,主要是农轻重、工业内部、生产与基建、积累与消费等比例关系;巩固已经取得的经济建设成果;充实那些以工业品为原料的轻工业和手工业品的生产,发展塑料、化纤等新兴工业;提高产品质量,改善企业管理,提高劳动生产率.“八字方针”的中心是调整.1年前查看全部
- 在《出师表》中,诸葛亮主张在外交、内政方面应遵循的方针是_____,_____,_____.(用原文填空)
 艾里西亚1年前1
艾里西亚1年前1 -
 沐书 共回答了16个问题
沐书 共回答了16个问题 |采纳率93.8%三条建议是:
①开张圣听(广开言路);
②严明赏罚(赏罚分明);
③亲贤臣,远小人( 亲贤远佞)1年前查看全部
- 从8:55到9:15,钟表的方针转动的角度是120°,时针转动的角度是( )?
 hs46101年前2
hs46101年前2 -
 黄天云 共回答了17个问题
黄天云 共回答了17个问题 |采纳率76.5%从8:55到9:15,钟表的方针转动的角度是120°,时针转动的角度是( 10º)?
120÷12=10º1年前查看全部
- 双百方针中的双百指的是什么?
 度是04231年前1
度是04231年前1 -
 h王者之风 共回答了13个问题
h王者之风 共回答了13个问题 |采纳率92.3%百花齐放 百家争鸣1年前查看全部
- 要中考了。求学霸给我提学习方针
 wolf3301年前2
wolf3301年前2 -
 xinwu123 共回答了808个问题
xinwu123 共回答了808个问题 |采纳率0.2%我个人认为学习方针适合自己才是好的,虽然这话很没水平,但这是事实,我班里有学霸能整天做作业;还有做作业速度超快,做完就看课外书的;这些都是很难学的,因此只要能让自己每天都有进步即可,可以买教辅啊1年前查看全部
- 中国共产党的文化工作基本方针是A、向科学进军 B、古为今用,洋为中用 C、百花齐放,百家争鸣 D、德、智、体全面发展
 yrdyjwx1年前1
yrdyjwx1年前1 -
 对月明 共回答了22个问题
对月明 共回答了22个问题 |采纳率81.8%如果是单选题的话应该选C,“双百方针’
多选的话选ABC.
中国共产党文化工作的基本方针包括两点:
第一,发展民族的科学的大众的文化.
第二,百花齐放,百家争鸣;古为今用,洋为中用.
D项是教育方针.1年前查看全部
- 面对全球气候变化,我们应该采取的措施和方针是什么
 66656331年前1
66656331年前1 -
 ee基本靠手 共回答了14个问题
ee基本靠手 共回答了14个问题 |采纳率92.9%(1)使用天然气等清洁能源,减少二氧化碳等温室气体的排放.
(2)大力发展科技,进行煤的气化和液化以及脱硫处理.
(3)积极发展公共交通,限制私家车出行,对工业排放进行严格监测.
(4)大力植树造林,增加城市绿地和水域面积.
(5)加强国际合作,各国承担共同而有差别的任务.1年前查看全部
- "团结——批评——团结”是解决人民内部矛盾的真确方针,破折号的作用是什么?
 angeline0301年前1
angeline0301年前1 -
 nlaq187 共回答了16个问题
nlaq187 共回答了16个问题 |采纳率93.8%表意思递进(紧承)
“团结──批评──团结”意思逐层深入,表示:从团结的愿望出发,经过批评,达到新的团结.破折号用法当然表示递进.1年前查看全部
- 数学计算应用x+y=632x+1.5y=100这是来自于针织毛衣中的一个收方针的工艺计算,要求:1.假设你没有学过方程解
数学计算应用
x+y=63
2x+1.5y=100
这是来自于针织毛衣中的一个收方针的工艺计算,
要求:1.假设你没有学过方程解法
2.用普通计算器,通过加减乘除的运算将答案算出; Cyy20071年前4
Cyy20071年前4 -
 sunspider 共回答了20个问题
sunspider 共回答了20个问题 |采纳率85%x+y=63
2x+2y=126
2x+1.5y=100
0.5y=26
y=52
x=111年前查看全部
- 某校六年级二班同学在阅读西游记时对猪八戒这个人物有两种不同看法为此语文老师组织了一场辩论假如你是正方针对下面反方辩词该怎
某校六年级二班同学在阅读西游记时对猪八戒这个人物有两种不同看法为此语文老师组织了一场辩论假如你是正方针对下面反方辩词该怎么说起
 Wangxinjie1081年前0
Wangxinjie1081年前0 -
 共回答了个问题
共回答了个问题 |采纳率
- 分别写出依法治国的"新,老十六字方针"并简要说明二者的不同
 荣光夺目1年前1
荣光夺目1年前1 -
 nmox2_6dca6f_29 共回答了10个问题
nmox2_6dca6f_29 共回答了10个问题 |采纳率100%0回答 17 秒钟前
建筑建材网里监理对于季度评分怎么评
0回答 6 秒钟前
怎样学习珠心算1年前查看全部
- 设n阶方针A满足A^2-5A+5E=0.证明矩阵A-2E可逆,并求其逆矩阵
 无言花1年前1
无言花1年前1 -
 zhoumannan 共回答了14个问题
zhoumannan 共回答了14个问题 |采纳率92.9%因为 A^2-5A+5E=0
所以 A(A-2E)-3(A-2E)-E=0
所以 (A-3E)(A-2E)=E
所以 A-2E 可逆,且(A-2E)^-1 = A-3E1年前查看全部
- 有关线性代数的一道题目,设二阶方针A的特征值为1,-1.,相应的特征向量分别为a1(1,1)T,a2(0,1)T.求A的
有关线性代数的一道题目,设二阶方针A的特征值为1,-1.,相应的特征向量分别为a1(1,1)T,a2(0,1)T.求A的五
求A的五次幂 starduoduo1年前2
starduoduo1年前2 -
 wolfQQQ 共回答了15个问题
wolfQQQ 共回答了15个问题 |采纳率93.3%因为P^(-1)AP=对角阵(1,-1)
所以A=P*对角阵(1,-1)*P^(-1)
因此A的5次幂= P*对角阵(1,-1)的5次幂*P^(-1)
=矩阵1 0 乘以“对角阵(1,-1)的5次幂”乘以矩阵1 0的逆矩阵
1 1 1 1
=矩阵1 0 乘以“对角阵(1,-1)”乘以矩阵1 0
1 1 - 1 1
=1 0
2 -1
不好输入,抱歉!1年前查看全部
- 英语翻译首先,我们的产品定价略高于同行一般产品.我们以提高中端市场占有率为主要方针,依靠适销对路的方法去增加我们的品牌优
英语翻译
首先,我们的产品定价略高于同行一般产品.我们以提高中端市场占有率为主要方针,依靠适销对路的方法去增加我们的品牌优势.我们的目标客户群是定位在追求健康美丽时尚的女性身上,她们追求健康美容养生,同时对小礼物会比较感兴趣.因此我们选择大型商场作为我们主要推销点.我们将会在新产品上市的同期在各个城市的大型商场举办关于“美容健康”的知识科普讲座,在科普美容养生的知识同时推广我们的红茶饮料.在顾客停留在我们宣传区的范围内时,可以免费品尝我们的红茶饮料.于此同时,在讲座的旁边则是我们的新产品推销台.如果您购买一定数量的产品,我们还将会有精美的小礼物赠送.
通过这样的一个产品战略和推广方式,不但可以提高我们的品牌知名度,而且能够很好的把我们的新产品推出市场. sunny12345671年前1
sunny12345671年前1 -
 yeahbaby_21 共回答了15个问题
yeahbaby_21 共回答了15个问题 |采纳率93.3%First, product pricing is slightly higher than that of ordinary products we peer. We have to improve in the end market share as main policy, relying on marketable to increase our brand advantage. Our target customer group is located in the pursuit of health and beauty of fashion women, their pursuit of health and beauty regimen, the small gift might be interested. So we choose large shopping malls as our main selling point. We will be in the same period of new products listed in the city's major shopping malls have knowledge lecture on "beauty and health", in the popular beauty health knowledge and promote our black tea beverage. Stay in our propaganda area when the customers can enjoy free of charge, our black tea beverage. At the same time, in the next lecture is our new product promotion platform. If you buy a certain number of products, we will also have a little gift of exquisite gift.
Through a product strategy and promotion in this way, not only can improve the visibility of our brand, but also good to put our new product on the market.1年前查看全部
- 英语翻译英文翻译~公司司训~质量方针英文翻译~公司司训~质量方针
 小木鱼是我1年前2
小木鱼是我1年前2 -
 我还是静子 共回答了20个问题
我还是静子 共回答了20个问题 |采纳率85%Company Motto
Quality Policy1年前查看全部
- 《隆中对》一文中诸葛亮为刘备提出的战略方针是什么
 xiaofly981年前1
xiaofly981年前1 -
 和风情有约 共回答了20个问题
和风情有约 共回答了20个问题 |采纳率75%跨有荆、益,保其岩阻,西和诸戎,南抚夷越,外结好孙权,内修整理,天下有变,则命一上将将荆州之军以向宛、洛,将军身率益州之众出于秦川”.
整个成就霸业的战略分三步走:第一步,跨有荆、益,保其岩阻——建立稳固的根据地;第二步,西和诸戎,南抚夷越,外结好孙权,内修政理——稳定后方,做好内政外交上的准备;第三步,天下有变,则命一上将将荆州之军以向宛、洛,将军身率益州之众出于秦川——北定中原,成就霸业.1年前查看全部
- 一国两制是我国解决港澳台问题的基本方针吗
 shadowlain1年前1
shadowlain1年前1 -
 5跳跳荡秋千 共回答了16个问题
5跳跳荡秋千 共回答了16个问题 |采纳率87.5%对啦!一国两制、港人冶港、50年不变.
香港的全称是中华人民共和国香港特别行政区(Hong Kong Special Administrative Region,简称HKSAR),香港自秦朝起明确成为当时的中原领土,直至19世纪中叶清朝对外战败,领域分批被割让及租借予英国成为殖民地,香港从而开通港口发展.1980年代,中、英两国落实香港前途问题,于1984年签订《中英联合声明》,决定1997年7月1日中华人民共和国对香港恢复行使主权.中方承诺在香港实行一国两制,香港将保持资本主义制度和原有的生活方式,并享受外交及国防以外所有事务的高度自治权,也就是“港人治港、高度自治”.1年前查看全部
- 实验室中常采用常温下分解过氧化氢(双氧水)溶液(二氧化锰作催化剂)或加热高锰酸钾的方针制取氧气.
实验室中常采用常温下分解过氧化氢(双氧水)溶液(二氧化锰作催化剂)或加热高锰酸钾的方针制取氧气.
(1)请计算:制取3.2g氧气,理论上需高锰酸钾的质量为多少?需质量分数为30%的过氧化氢的质量为多少?
(2)某化学试剂公司报价:高锰酸钾30.50元/kg,30%过氧化氢溶液21.70元/kg.请你从实验操作和制取成本两方面分析并判断,用哪一种方法制取氧气更好,这种方法的主要优点是什么?(二氧化锰价格低、消耗少、能重复用,可忽略不计) 0539muzi1年前1
0539muzi1年前1 -
 春天的黄水仙 共回答了21个问题
春天的黄水仙 共回答了21个问题 |采纳率95.2%解题思路:(1)根据氧气的质量通过方程式计算出需高锰酸钾和过氧化氢的质量;
(2)根据过氧化氢制氧气的装置和高锰酸钾制取氧气的装置图的比较考虑,再根据制取相同质量的氧气需要它们的价格考虑.(1)设要制取3.2g氧气需要高锰酸钾质量为x,需要过氧化氢质量为y
2KMnO4
△
.
K2MnO4+MnO2+O2↑
316 32
x3.2g
根据:[316/x=
32
3.2g]
解得x=31.6g
2H2O2
MnO2
.
2H2O+O2↑
6832
y 3.2g
根据:[68/32=
y
3.2g]
解得Y=6.8g,所以需质量分数为30%过氧化氢溶液的质量为:[6.8g/30%]=22.7g;
(2)由于过氧化氢制氧气不需加热,操作简单,并且制取相同质量(3.2g)O2时购买H2O2(约0.49元)比KMnO4(约0.96元)价格低.
故答案为:(1)理论上需高锰酸钾的质量为31.6g,需质量分数为30%的过氧化氢的质量为22.7g;
(2)采用双氧水制取氧气效果较好,原因是双氧水制取氧气操作简单且价格便宜;点评:
本题考点: 根据化学反应方程式的计算.
考点点评: 根据化学反应方程式的计算的审题是非常关键的,一般是抓住“三找”;即一找化学反应方程式,二找已知量和未知量x,三找用到的相对质量关系,同时注意解题步骤和格式.1年前查看全部
- 根据“因地制宜”的方针,下列地区与应种植农作物搭配正确的一组是 [
根据“因地制宜”的方针,下列地区与应种植农作物搭配正确的一组是 []A.山东半岛--水稻、花生、橡胶
B.四川盆地--甘蔗、水稻、甜菜
C.洞庭湖平原--春小麦、油菜、水稻
D.松嫩平原--春小麦、大豆、甜菜 cz1131年前1
cz1131年前1 -
 tnf4180 共回答了16个问题
tnf4180 共回答了16个问题 |采纳率81.3%D1年前查看全部
- 请选出各题中没有语病的一句: A.创刊一年来,该报针对行业特点,遵循“指导性强、信息量大”的办报方针,取得了很大成绩,被
请选出各题中没有语病的一句:
a.创刊一年来,该报针对行业特点,遵循“指导性强、信息量大”的办报方针,取得了很大成绩,被***部、新闻出版署誉为“导向好、品位高”。 b.如果不及时采取有效措施,人为的蓄意破坏以及恶劣天气变化,都可能引发更为严重的灾难性后果。 c.植树节这天,学校的几个***都来到了植树现场。 d.柳敬亭不是一个很有家教、素质不高的人,但他不怕挫折,凭自己的努力成为很负盛名的说书家。  wlwlxiaoyu1年前1
wlwlxiaoyu1年前1 -
 那帅哥是我的 共回答了21个问题
那帅哥是我的 共回答了21个问题 |采纳率95.2%C
(A“誉为”缺宾语;B“人为的”与“蓄意”重复;D项前半句否定不当,后半句“很负盛名”语义重复;)1年前查看全部
- 在社会主义改造基本完成以后,正确处理人民内部矛盾成为国家政治生活的主题.中国共产党提出的正确处理人民内部矛盾的方针政策中
在社会主义改造基本完成以后,正确处理人民内部矛盾成为国家政治生活的主题.中国共产党提出的正确处理人民内部矛盾的方针政策中不包括的是( ) A .统筹兼顾,适当安排 B .有理、有利、有节 C .百花齐放,百家争鸣 D .长期共存,互相监督
 yyyyyyyyii1年前1
yyyyyyyyii1年前1 -
 kaivsxie 共回答了15个问题
kaivsxie 共回答了15个问题 |采纳率100%B正确处理人民内部矛盾的具体方针:在经济上,实行“统筹兼顾,适当安排”的方针;在共产党与民主党派关系上,实行“长期共存,互相监督”的方针;在科学文化工作上,实行“百花齐放,百家争鸣”的方针.选项B是抗战时期同顽固派做斗争的原则1年前查看全部
- 质量管理中的二十字方针指什么?是不是发现问题、查明原因、采取措施、纳入标准、不再发生?
 qinzhizhen191年前1
qinzhizhen191年前1 -
 哭了疯了 共回答了18个问题
哭了疯了 共回答了18个问题 |采纳率83.3%没错的,更准确的说是SPC应当遵循的20字方针.1年前查看全部
- 英语学过好多遍都不会 我想从头开始学 不知道应该怎么学 看什么书 我想说的是从零点开始学 有没有什么方针
 spring8210061年前1
spring8210061年前1 -
 宝贝薇我爱你 共回答了20个问题
宝贝薇我爱你 共回答了20个问题 |采纳率95%就拿最初的课本(比如刚学音标和字母时的那些书)就可以,再找个参考书,其实最好是买上最初级的课本,找个辅导老师.1年前查看全部
- 有一实心方针,每边棋子20枚,现增加棋子30枚,摆成五层空心方针,求最外层和最里层各有多少棋子?
 michengbaobao1年前2
michengbaobao1年前2 -
 tt8nn 共回答了19个问题
tt8nn 共回答了19个问题 |采纳率73.7%设最外层有 x 枚棋子,则从外到内五层棋子数分别为 x、x-4、x-8、x-12、x-16 ,
实心方针,每边棋子 20 枚,则共有 20*20 枚棋子;
可列方程:x+(x-4)+(x-8)+(x-12)+(x-16) = 20*20+30 ,
解得:x = 94 ,可得:x-16 = 78 ,
即:最外层有 94 枚棋子,最里层有 78 枚棋子.1年前查看全部
- 与隆中对有关的问题诸葛亮提出的近期的策略目标是( ),最终的策略目标是( ),他主张在内政方面应遵循的方针是( ),外交
与隆中对有关的问题
诸葛亮提出的近期的策略目标是( ),最终的策略目标是( ),他主张在内政方面应遵循的方针是( ),外交方面的方针是( ),等到形势发生变化,在兵分两路出击:一路是( ),另一路是( ) liyunone1年前1
liyunone1年前1 -
 popsy 共回答了17个问题
popsy 共回答了17个问题 |采纳率82.4%跨有荆益
兴复汉室,成就霸业
内修政理
西和诸戎,南抚夷越,外结好孙权
从荆州向宛、洛,从益州出秦川1年前查看全部
- 贯彻四个尊重方针的重要性不要太多,短小精悍
 zhlyyy1年前1
zhlyyy1年前1 -
 kerte 共回答了20个问题
kerte 共回答了20个问题 |采纳率95%四个尊重"方针的重要性:(1),劳动是人类生存和发展所需要的财富的源泉,也是产生和积累知识,发展和孕育人才,凝聚和提供创造力的源泉.(2),知识是创造财富的重要资源.(3)人才是创造财富的最重要的资源.(4),创造是人类社会不断发展的内驱力.1年前查看全部
- 请问:设A为2阶可逆方针,A*为A的伴随矩阵,若|A|=1,则|A*-3A^(-1)|=?
 哀虫1年前2
哀虫1年前2 -
 gys2004291 共回答了15个问题
gys2004291 共回答了15个问题 |采纳率93.3%因为 A*=|A|A^-1=A^-1
所以 |A*-3A^-1|
= |A^-1-3A^-1|
= |-2A^-1|
= (-2)^2|A|^-1
= -4.1年前查看全部
- 中国在万隆会议上提出“求同存异”的方针,表明中国执行的是:A:社会主义外交原则 B:平等互利外交原则 C:和平共处五项原
中国在万隆会议上提出“求同存异”的方针,表明中国执行的是:A:社会主义外交原则 B:平等互利外交原则 C:和平共处五项原则 D:务实外交原则 D 那什么是务实外交原则呢?
 傻瓜猫1241年前1
傻瓜猫1241年前1 -
 lucky_216 共回答了18个问题
lucky_216 共回答了18个问题 |采纳率100%中国在万隆会议上提出了“求同存异”的方针,表明中国执行的是务实外交原则.(Y)
、“求同存异”方针中求同的基础是:殖民主义的痛苦和灾难.(Y)
这原来是道判断题 ,是概念 ,背下来就好了1年前查看全部
- ★多选题:>1中国共产党实行的抗日民族统一战线策略总方针是 A.发展进步势力 B.争取中间势力 C.孤立顽固势力 D.又
★多选题:>
1中国共产党实行的抗日民族统一战线策略总方针是
A.发展进步势力
B.争取中间势力
C.孤立顽固势力
D.又联合又斗争
E.以斗争求团结
★多选题:>
2我国人民民主专政的主要特点是
A.民主与集中的相互结合
B.衔接民主革命和社会主义革命两个阶段
C.扩大对敌人专政的范围
D.扩大人民民主的范围
E.在概念表述上准确鲜明
★多选题:>
3毛泽东同志在下列那些文章中提到人民民主专政
A、《青年运动的方向》
B、《论人民民主专政》
C、《将革命进行到底》
D、《论联合政府》
★多选题:>
4我国社会主义改造的对象是
A、个体农业
B、官僚资本主义
C、个体手工业
D、资本主义工商业
E、小资产阶级
5★多选题:>
“四马分肥”是指
A、所得税
B、企业公积金
C、工人福利基金
D、资本家的利润(包括股息和红利)
E、奖金
现在的第四答案ACD 和第五题的ABCD答案是对的 2, popart1年前1
popart1年前1 -
 3儿gh环境 共回答了21个问题
3儿gh环境 共回答了21个问题 |采纳率95.2%1 ABDE 2 BDE 3 CD 4 ACD 5. ABCD1年前查看全部
- 隆中对中诸葛亮为了达到这个目标提出的战略方针是什么
 寂海陌1年前1
寂海陌1年前1 -
 hehe_147 共回答了19个问题
hehe_147 共回答了19个问题 |采纳率100%取吴抗曹,取荆、益二州,与周边和睦相处1年前查看全部
- 刘备三顾茅庐请得诸葛亮加入,得出隆中对的战略方针,大概是在公元多少年
 ntgnnms1年前1
ntgnnms1年前1 -
 takiy 共回答了15个问题
takiy 共回答了15个问题 |采纳率100%隆中对,的事情发生在建安十二年(207年),刘备三顾茅庐,诸葛亮(当时27岁)对刘备陈说三分天下之计1年前查看全部
- 从思想路线、政治路线和经济方针三个方面,说明中共十一届三中全会的内容
 patrist1年前1
patrist1年前1 -
 甲由申田 共回答了18个问题
甲由申田 共回答了18个问题 |采纳率94.4%第一,全会实现了思想路线的拨乱反正.思想路线的拨乱反正是各方面拨乱反正的前提和先导.全会冲破了党的指导思想上存在的教条主义和个人崇拜的严重束缚,坚决批判和否定了“两个凡是”的错误方针,高度评价了关于真理标准问题的讨论,指出实践是检验真理的唯一标准是党的思想路线的根本原则,从而重新确立了马克思主义的实事求是的思想路线.会议在充分肯定毛泽东同志在我国长期革命斗争中的巨大作用的同时,着重强调要从科学体系上掌握和运用毛泽东思想,不能一切照搬照抄,不能搞“两个凡是”.否则,党和国家就会失去生机,就要亡党亡国.全会指出:“党中央在理论战线上的崇高任务,就是领导、教育全党和全国人民历史地科学地认识毛泽东同志的伟大功绩,完整地、准确地掌握毛泽东思想的科学体系,把马列主义、毛泽东思想的普遍原理同社会主义现代化建设的具体实践结合起来,并在新的历史条件下加以发展.”
第二,全会实现了政治路线的拨乱反正.这是最根本的拨乱反正.建国之初,党就要求各项工作必须以发展生产力为中心.党的八大确定要以在新的生产关系下保护和发展生产力为主要任务.这以后我们的失误,归根到底,就是背离了八大路线,搞了“以阶级斗争为纲”,没有集中力量进行经济建设.三中全会果断地作出把全党工作着重点和全国人民的注意力转移到社会主义现代化建设上来的战略决策.这是八大正确路线的恢复和发展,是在新的历史条件下对建设有中国自己特色社会主义道路的探索.
第三,全会作出了实行改革开放的新决策,启动了农村改革的新进程.全会在讨论1979、1980两年的国民经济计划安排时,提出了要注意解决国民经济重大比例失调,搞好综合平衡的要求.全会还讨论了农业问题,认为农业这个国民经济的基础就整体来说还十分薄弱,只有大力恢复和加快发展农业生产,才能提高全国人民的生活水平.全会提出了当前发展农业的一系列政策措施,并同意将《中共中央关于加快农业发展若干问题的决定(草案)》等文件发到各省、市、自治区讨论和试行.这个文件在经过修改和充实之后正式发布,接着一些重要的农业方面的文件相继制定和发布施行,有力地推动了农村改革的进程
给你总结下 思想路线:纠正左倾错误
政治路线:从以阶级斗争为纲转到以经济建设为中心
经济方针:改革开放1年前查看全部
- 十一届三中全会以来,我党制定的一系列正确的路线、方针、政策促进了我国经济的迅猛发展,这说明:
十一届三中全会以来,我党制定的一系列正确的路线、方针、政策促进了我国经济的迅猛发展,这说明:
A.经济基础发展的道路是由上层建筑决定的
B.上层建筑的发展决定经济基础的发展方向
C.上层建筑对经济基础具有积极的能动作用
D.社会主义社会的发展不受经济基础决定上层建筑规律的制约 屯子人1年前1
屯子人1年前1 -
 20cl 共回答了29个问题
20cl 共回答了29个问题 |采纳率86.2%C.上层建筑对经济基础具有积极的能动作用1年前查看全部
- 马克思哲学原理辨析题:对于党的方针、政策必须坚决“一刀切”地加以贯彻执行.
 Thinkvista1年前1
Thinkvista1年前1 -
 糯米哆哆 共回答了16个问题
糯米哆哆 共回答了16个问题 |采纳率87.5%按照马克思主义,要辩证看,不同地方环境、资源都不一样,方针政策也应该不一样.搞一刀切是违背马克思主义基本原理的1年前查看全部
- 《毛概》作业4多选7-87. 繁荣科学文化的基本方针包括A. “中学为体、西学为用”B. “百花齐放、百家争鸣”C. “
《毛概》作业4多选7-8
7. 繁荣科学文化的基本方针包括
a. “中学为体、西学为用”
b. “百花齐放、百家争鸣”
c. “古为今用、洋为中用”
d. “大鸣大放”
8. 1956年毛***在《论十大关系》中第一次提出了中******和各******要
a. 长期共存
b. 互相监督
c. 肝胆相照
d. 荣辱与共
e. 同舟共济 stella_w1年前1
stella_w1年前1 -
 xinantianzhen 共回答了22个问题
xinantianzhen 共回答了22个问题 |采纳率86.4%7、B
8、AB1年前查看全部
- 英语翻译中文:确定对外合作项目,要根据自己的条件和特点,符合本社的出版方针和出书范围.我的英语翻译:The identi
英语翻译
中文:确定对外合作项目,要根据自己的条件和特点,符合本社的出版方针和出书范围.
我的英语翻译:
The identification of external cooperation should in accordance with its own conditions and features,meeting the agency's publication policy and scope.
欢迎踊跃回答,多提宝贵意见. 鑫漪1年前3
鑫漪1年前3 -
 那晚蓝月亮 共回答了18个问题
那晚蓝月亮 共回答了18个问题 |采纳率83.3%楼上要是老师,我就是教授了,明显没有谓语动词的句子你也说很准确
我的建议:
去掉The identification of
直接用External cooperation作为主语
谓语部分should be in ...
或者should accord with ...
如果是出版社建议用press1年前查看全部
- 阅读下列材料:材料一 党的十八大提出坚持节约资源和保护环境的基本国策,坚持节约优先、保护优先、自然恢复为主的方针……为人
阅读下列材料:
材料一 党的十八大提出坚持节约资源和保护环境的基本国策,坚持节约优先、保护优先、自然恢复为主的方针……为人民创造良好生产生活环境,为全球生态安全作出贡献。网友们认为:建设生态文明要靠群众也要靠政府。
(1)结合材料一,请你运用《政治生活》的知识,论证建设生态文明要靠政府的合理性。(12分)
材料二 在当前,国家大力倡导建设“两型”社会,发展绿色节能环保产业的情况下,一些地方比项目、扩产能的意图比较强烈。因此,一些高耗能、高污染的行业生产和出口以及投资增长都比较迅速,这势必导致能源消耗快速增长。与此同时,一些地方对节能减排工作仍然存在认识不到位、责任不明确、措施不配套、政策不完善、投入不落实、协调不得力等问题。可以说,我国节能减排的形势非常严峻。
(2)在节能问题上,不同部门有着不同的职责。结合材料二,依照要求,运用《政治生活》知识,填写下表。(13分)具体部门 应该怎样做 为什么这样做 中共中央 中国共产党是执政党,是中国特色社会主义事业的领导核心 全国人大 制定相关法律,监督法律的实施和其他国家机关的工作 国务院 人民政协  水凝香尘1年前1
水凝香尘1年前1 -
 狼忍不发 共回答了18个问题
狼忍不发 共回答了18个问题 |采纳率83.3%(1)①我国是人民民主专政的社会主义国家,我国政府是为人民服务的政府。建设生态文明是政府维护国家利益和人民利益的重要表现。
②我国政府以为人民服务为宗旨,政府要坚持对人民负责原则。建设生态文明,提高人民群众的生活质量是政府的宗旨和原则的要求。
③我国政府具有组织社会主义经济建设、提供社会公共服务的职能。建设生态文明是政府履行管理和服务职能的要求。
④我国政府坚持依法行政,科学民主决策。建设生态文明要靠政府具有合理性(每个要点3分)
(2)
具体部门
应该怎样做
为什么这样做
中共中央
制定大政方针,推进科学发展、提出立法建议(2分)
中国共产党是执政党,是中国特色社会主义事业的领导核心
全国人大
制定相关法律,监督法律的实施和其他国家机关的工作
全国人民代表大会是最高国家权力机关,拥有最高立法权和最高监督权(2分)
国务院
坚持对人民负责和依法行政的原则,依法履行好政府职能(2分)
国务院是我国的中央人民政府,是最高国家权力机关的执行机关,是人民意旨的执行者和利益的捍卫者(3分)
人民政协
履行政治协商、民主监督、参政议政职能(2分)
人民政协是我国的爱国统一战线组织,是发扬社会主义民主的重要形式(2分)
第(1)问考查学生运用政府的相关知识分析和探讨问题的能力,可从政府的性质、宗旨和原则、职能以及科学民主决策等方面回答。第(2)问以填表的形式考查学生运用中国共产党、全国人大、我国政府以及人民政协的知识解决问题的能力,作答时一定要看清主体,准确对号入座。1年前查看全部
- 教育目的与教育方针的关系是( 教育目的与教育方针的关系是( )a.教育目的是教育方针的指导原则b.教育目的包含教育方针c
教育目的与教育方针的关系是(
教育目的与教育方针的关系是( )
a.教育目的是教育方针的指导原则b.教育目的包含教育方针
c.教育目的规定教育方针d.教育目的是教育方针的组成部分 gdgszyb1年前1
gdgszyb1年前1 -
 mybestwids 共回答了24个问题
mybestwids 共回答了24个问题 |采纳率95.8%d1年前查看全部
大家在问
- 1(2008•青海)用弹簧测力计在空气中称得一石块重1N,将石块完全没入水中后,弹簧测力计示数为0.6N,则石块在水中受到
- 2仓库有一批物资,第一次调出480件,第二次调出余下的8分之3,这时剩下的件数与调出的比是5:7.这批物资
- 3请在这里概述您的问题已知ⅹ,y满足
- 4高数-解方程组x-y+z=1与2x+y+z=4所组成的方程组的解
- 53.填空 1)课文以 为线索,按 的顺序,先写 ,再写 ,从抒写 之情到 之憾到 之感,脉络分明,结构严谨.
- 6介绍武夷山的英语文章最好带翻译 谢咯
- 7小轿车多呈流线型外形如下图所示。在快速行驶中不仅能使受到的气流阻力减小,还会因为汽车上方的流速比汽车下方气流流速
- 8夏天刚刚下完雨 怎么改为比喻句?
- 9设a是实数,试讨论关于x的方程lg(x-1)+lg(3-x)=lg(a-x)的实根的个数.
- 10设P是△ABC内一点,三个顶点到对边的距离分别为h A 、h B 、h C ,P到对应三边的距离依次为l a 、l b
- 11sin3a与sina的关系
- 12如果2mx^ay与-5nx^(2a-3 )y是关于x,y的单项式,且它们是同类项,求(7a-22)^2006的值
- 13Do they have any old photos in their room 写出同义句 There are no
- 149x+1-x=5.5
- 15某房子基价为2580元 一 平方米
